Analytic number theory is often concerned with the asymptotic behaviour of various arithmetic functions: functions or
from the natural numbers
to the real numbers
or complex numbers
. In this post, we will focus on the purely algebraic properties of these functions, and for reasons that will become clear later, it will be convenient to generalise the notion of an arithmetic function to functions
taking values in some abstract commutative ring
. In this setting, we can add or multiply two arithmetic functions
to obtain further arithmetic functions
, and we can also form the Dirichlet convolution
by the usual formula
Regardless of what commutative ring is in used here, we observe that Dirichlet convolution is commutative, associative, and bilinear over
.
An important class of arithmetic functions in analytic number theory are the multiplicative functions, that is to say the arithmetic functions such that
and
for all coprime . A subclass of these functions are the completely multiplicative functions, in which the restriction that
be coprime is dropped. Basic examples of completely multiplicative functions (in the classical setting
) include
- the Kronecker delta
, defined by setting
for
and
otherwise;
- the constant function
and the linear function
(which by abuse of notation we denote by
);
- more generally monomials
for any fixed complex number
(in particular, the “Archimedean characters”
for any fixed
), which by abuse of notation we denote by
;
- Dirichlet characters
;
- the Liouville function
;
- the indicator function of the
–smooth numbers (numbers whose prime factors are all at most
), for some given
; and
- the indicator function of the
–rough numbers (numbers whose prime factors are all greater than
), for some given
.
Examples of multiplicative functions that are not completely multiplicative include
- the Möbius function
;
- the divisor function
(also referred to as
);
- more generally, the higher order divisor functions
for
;
- the Euler totient function
;
- the number of roots
of a given polynomial
defined over
;
- more generally, the point counting function
of a given algebraic variety
defined over
(closely tied to the Hasse-Weil zeta function of
);
- the function
that counts the number of representations of
as the sum of two squares;
- more generally, the function that maps a natural number
to the number of ideals in a given number field
of absolute norm
(closely tied to the Dedekind zeta function of
).
These multiplicative functions interact well with the multiplication and convolution operations: if are multiplicative, then so are
and
, and if
is completely multiplicative, then we also have
Finally, the product of completely multiplicative functions is again completely multiplicative. On the other hand, the sum of two multiplicative functions will never be multiplicative (just look at what happens at ), and the convolution of two completely multiplicative functions will usually just be multiplicative rather than completley multiplicative.
The specific multiplicative functions listed above are also related to each other by various important identities, for instance
where is an arbitrary arithmetic function.
On the other hand, analytic number theory also is very interested in certain arithmetic functions that are not exactly multiplicative (and certainly not completely multiplicative). One particularly important such function is the von Mangoldt function . This function is certainly not multiplicative, but is clearly closely related to such functions via such identities as
and
, where
is the natural logarithm function. The purpose of this post is to point out that functions such as the von Mangoldt function lie in a class closely related to multiplicative functions, which I will call the derived multiplicative functions. More precisely:
Definition 1 A derived multiplicative function
is an arithmetic function that can be expressed as the formal derivative
at the origin of a family
of multiplicative functions
parameterised by a formal parameter
. Equivalently,
is a derived multiplicative function if it is the
coefficient of a multiplicative function in the extension
of
by a nilpotent infinitesimal
; in other words, there exists an arithmetic function
such that the arithmetic function
is multiplicative, or equivalently that
is multiplicative and one has the Leibniz rule
More generally, for any
, a
-derived multiplicative function
is an arithmetic function that can be expressed as the formal derivative
at the origin of a family
of multiplicative functions
parameterised by formal parameters
. Equivalently,
is the
coefficient of a multiplicative function in the extension
of
by
nilpotent infinitesimals
.
We define the notion of a
-derived completely multiplicative function similarly by replacing “multiplicative” with “completely multiplicative” in the above discussion.
There are Leibniz rules similar to (2) but they are harder to state; for instance, a doubly derived multiplicative function comes with singly derived multiplicative functions
and a multiplicative function
such that
for all coprime .
One can then check that the von Mangoldt function is a derived multiplicative function, because
is multiplicative in the ring
with one infinitesimal
. Similarly, the logarithm function
is derived completely multiplicative because
is completely multiplicative in
. More generally, any additive function
is derived multiplicative because it is the top order coefficient of
.
Remark 1 One can also phrase these concepts in terms of the formal Dirichlet series
associated to an arithmetic function
. A function
is multiplicative if
admits a (formal) Euler product;
is derived multiplicative if
is the (formal) first logarithmic derivative of an Euler product with respect to some parameter (not necessarily
, although this is certainly an option); and so forth.
Using the definition of a -derived multiplicative function as the top order coefficient of a multiplicative function of a ring with
infinitesimals, it is easy to see that the product or convolution of a
-derived multiplicative function
and a
-derived multiplicative function
is necessarily a
-derived multiplicative function (again taking values in
). Thus, for instance, the higher-order von Mangoldt functions
are
-derived multiplicative functions, because
is a
-derived completely multiplicative function. More explicitly,
is the top order coeffiicent of the completely multiplicative function
, and
is the top order coefficient of the multiplicative function
, with both functions taking values in the ring
of complex numbers with
infinitesimals
attached.
It then turns out that most (if not all) of the basic identities used by analytic number theorists concerning derived multiplicative functions, can in fact be viewed as coefficients of identities involving purely multiplicative functions, with the latter identities being provable primarily from multiplicative identities, such as (1). This phenomenon is analogous to the one in linear algebra discussed in this previous blog post, in which many of the trace identities used there are derivatives of determinant identities. For instance, the Leibniz rule
for any arithmetic functions can be viewed as the top order term in
in the ring with one infinitesimal , and then we see that the Leibniz rule is a special case (or a derivative) of (1), since
is completely multiplicative. Similarly, the formulae
are top order terms of
and the variant formula is the top order term of
which can then be deduced from the previous identities by noting that the completely multiplicative function inverts
multiplicatively, and also noting that
annihilates
. The Selberg symmetry formula
which plays a key role in the Erdös-Selberg elementary proof of the prime number theorem (as discussed in this previous blog post), is the top order term of the identity
involving the multiplicative functions ,
,
,
with two infinitesimals
, and this identity can be proven while staying purely within the realm of multiplicative functions, by using the identities
and (1). Similarly for higher identities such as
which arise from expanding out using (1) and the above identities; we leave this as an exercise to the interested reader.
An analogous phenomenon arises for identities that are not purely multiplicative in nature due to the presence of truncations, such as the Vaughan identity
for any , where
is the restriction of a multiplicative function
to the natural numbers greater than
, and similarly for
,
,
. In this particular case, (4) is the top order coefficient of the identity
which can be easily derived from the identities and
. Similarly for the Heath-Brown identity
valid for natural numbers up to , where
and
are arbitrary parameters and
denotes the
-fold convolution of
, and discussed in this previous blog post; this is the top order coefficient of
and arises by first observing that
vanishes up to , and then expanding the left-hand side using the binomial formula and the identity
.
One consequence of this phenomenon is that identities involving derived multiplicative functions tend to have a dimensional consistency property: all terms in the identity have the same order of derivation in them. For instance, all the terms in the Selberg symmetry formula (3) are doubly derived functions, all the terms in the Vaughan identity (4) or the Heath-Brown identity (5) are singly derived functions, and so forth. One can then use dimensional analysis to help ensure that one has written down a key identity involving such functions correctly, much as is done in physics.
In addition to the dimensional analysis arising from the order of derivation, there is another dimensional analysis coming from the value of multiplicative functions at primes (which is more or less equivalent to the order of pole of the Dirichlet series at
). Let us say that a multiplicative function
has a pole of order
if one has
on the average for primes
, where we will be a bit vague as to what “on the average” means as it usually does not matter in applications. Thus for instance,
or
has a pole of order
(a simple pole),
or
has a pole of order
(i.e. neither a zero or a pole), Dirichlet characters also have a pole of order
(although this is slightly nontrivial, requiring Dirichlet’s theorem),
has a pole of order
(a simple zero),
has a pole of order
, and so forth. Note that the convolution of a multiplicative function with a pole of order
with a multiplicative function with a pole of order
will be a multiplicative function with a pole of order
. If there is no oscillation in the primes
(e.g. if
for all primes
, rather than on the average), it is also true that the product of a multiplicative function with a pole of order
with a multiplicative function with a pole of order
will be a multiplicative function with a pole of order
. The situation is significantly different though in the presence of oscillation; for instance, if
is a quadratic character then
has a pole of order
even though
has a pole of order
.
A -derived multiplicative function will then be said to have an underived pole of order
if it is the top order coefficient of a multiplicative function with a pole of order
; in terms of Dirichlet series, this roughly means that the Dirichlet series has a pole of order
at
. For instance, the singly derived multiplicative function
has an underived pole of order
, because it is the top order coefficient of
, which has a pole of order
; similarly
has an underived pole of order
, being the top order coefficient of
. More generally,
and
have underived poles of order
and
respectively for any
.
By taking top order coefficients, we then see that the convolution of a -derived multiplicative function with underived pole of order
and a
-derived multiplicative function with underived pole of order
is a
-derived multiplicative function with underived pole of order
. If there is no oscillation in the primes, the product of these functions will similarly have an underived pole of order
, for instance
has an underived pole of order
. We then have the dimensional consistency property that in any of the standard identities involving derived multiplicative functions, all terms not only have the same derived order, but also the same underived pole order. For instance, in (3), (4), (5) all terms have underived pole order
(with any Mobius function terms being counterbalanced by a matching term of
or
). This gives a second way to use dimensional analysis as a consistency check. For instance, any identity that involves a linear combination of
and
is suspect because the underived pole orders do not match (being
and
respectively), even though the derived orders match (both are
).
One caveat, though: this latter dimensional consistency breaks down for identities that involve infinitely many terms, such as Linnik’s identity
In this case, one can still rewrite things in terms of multiplicative functions as
so the former dimensional consistency is still maintained.
I thank Andrew Granville, Kannan Soundararajan, and Emmanuel Kowalski for helpful conversations on these topics.

20 comments
Comments feed for this article
24 September, 2014 at 2:59 pm
Eytan Paldi
It seems that the sum of two multiplicative functions can be multiplicative only if one of them is the constant function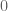 .
.
[By definition, multiplicative functions are required to take the value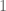 at
at 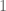 . -T.]
. -T.]
24 September, 2014 at 3:30 pm
Anonymous
Dear Prof. Tao, My browser (IE) mentions a parsing error for the formula preceding Remark 1.
[Corrected, thanks – T.]
24 September, 2014 at 6:59 pm
ACB
Should the second j in the sentence beginning, “Note that the convolution of a multiplicative function…” be a j’?
[Corrected, thanks – T.]
25 September, 2014 at 5:44 am
MrCactu5 (@MonsieurCactus)
If you don’t like the language of nilpotents, maybe just use matrices? Your epsilon can be written as
0 1
0 0
27 September, 2014 at 5:55 pm
David Roberts
Wouldn’t Hecke operators on modular curves be an example of a multiplicative function
on modular curves be an example of a multiplicative function  , considered as a map to endomorphisms of modular forms?
, considered as a map to endomorphisms of modular forms?
28 September, 2014 at 7:47 am
Terence Tao
Yes, this is an example. It looks like the corresponding endomorphism-valued Dirichlet series generates scalar Dirichlet series associated to various modular forms as coefficients using a basis of Hecke eigenforms, though this statement is basically tautological and I don’t know if one can do much with it that one can’t already do with the usual formulation of Hecke operators and eigenforms.
9 October, 2014 at 7:34 am
valuevar
Very nice! I was just wondering the other day – is there a name for the “higher identities” such as the one involving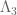 ? (I know about Diamond-Steinig identities for
? (I know about Diamond-Steinig identities for  .) I thought these identities were somehow associated with Bombieri, but that may be an association that existed partly in my head. (I’ve also heard some people crediting them to Faa di Bruno, who wrote down a chain rule for higher derivatives in the nineteenth century, but was not the first to do so.)
.) I thought these identities were somehow associated with Bombieri, but that may be an association that existed partly in my head. (I’ve also heard some people crediting them to Faa di Bruno, who wrote down a chain rule for higher derivatives in the nineteenth century, but was not the first to do so.)
9 October, 2014 at 8:00 am
Terence Tao
The identity explicitly appears in this 1975 paper of Bombieri: http://matwbn.icm.edu.pl/ksiazki/aa/aa28/aa2828.pdf . I don’t know if this is the earliest explicit appearance of it, though. For instance, Selberg already (implicitly) used the k=2 version of this formula in his 1949 proof of the prime number theorem in http://www.jstor.org/stable/1969455 , so I would find it plausible that he was aware of some version of the higher k identity also (but perhaps using different notation than the now-standard
explicitly appears in this 1975 paper of Bombieri: http://matwbn.icm.edu.pl/ksiazki/aa/aa28/aa2828.pdf . I don’t know if this is the earliest explicit appearance of it, though. For instance, Selberg already (implicitly) used the k=2 version of this formula in his 1949 proof of the prime number theorem in http://www.jstor.org/stable/1969455 , so I would find it plausible that he was aware of some version of the higher k identity also (but perhaps using different notation than the now-standard  ). Actually, I think the use of
). Actually, I think the use of  as a tool to detect k-almost primes even predates Selberg, though I’ll have to track down a precise reference for this…
as a tool to detect k-almost primes even predates Selberg, though I’ll have to track down a precise reference for this…
[UPDATE: I found the reference, but it turns out to postdate Selberg by a little bit: a close relative of the above identity appears in the 1956 PhD thesis of Golomb, “Problems in the distribution of the prime numbers”, in which it is observed that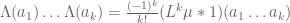 whenever
whenever  are coprime; see http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0022314X70900193 .]
are coprime; see http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0022314X70900193 .]
13 October, 2014 at 12:40 am
valuevar
This is helpful; thanks. However, for several applications (including at least some of those of Selberg, I believe) an identity involving $L^k\mu \ast 1$ has got $L^k$ attached to the wrong factor; it is much nicer to have it attached to $1$ rather than to $\mu$.
13 October, 2014 at 4:31 am
Mats Granvik
Möbius function calculated from arbitrary numbers as input:
http://math.stackexchange.com/questions/268159/m%c3%b6bius-function-from-random-number-sequence
27 November, 2014 at 7:58 pm
Fan
The use of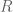 and
and 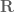 is inconsistent in Definition 1.
is inconsistent in Definition 1.
[Corrected, thanks – T.]
11 January, 2015 at 12:19 pm
Top 30 Computer Science and Programming Blogs | Yo Worlds
[…] 14. Terry Tao’s Blog: Terry Tao is a mathematician whose work is frequently relevant for computer scientists and computational theorists. Most of the posts are highly technical mathematical demonstrations that are not accessible to layman. This makes his blog an intellectually challenging but fruitful endeavor for the serious student of computer science or mathematics. Highlight: Derived Multiplicative Functions […]
17 May, 2015 at 7:11 am
Топ-30 лучших блогов о программировании… | IT News
[…] Что почитать на Terry Tao’s Blog: Производные мультипликативные функции […]
17 October, 2015 at 1:12 am
BLOGS ON COMPUTER SCIENCE | CS SECTION 6B 2013
[…] 14. Terry Tao’s Blog: Terry Tao is a mathematician whose work is frequently relevant for computer scientists and computational theorists. Most of the posts are highly technical mathematical demonstrations that are not accessible to layman. This makes his blog an intellectually challenging but fruitful endeavor for the serious student of computer science or mathematics. Highlight: Derived Multiplicative Functions […]
30 August, 2016 at 4:10 pm
Heuristic computation of correlations of the divisor function | What's new
[…] We remark that is an example of a derived multiplicative function, discussed in this previous blog post. […]
22 September, 2016 at 8:45 am
254A, Notes 1: Elementary multiplicative number theory | What's new
[…] also considers arithmetic functions taking values in more general rings than or , as in this previous blog post, but we will restrict attention here to the classical situation of real ofr complex arithmetic […]
31 October, 2017 at 9:08 pm
Computer science – Live Free
[…] 14. Terry Tao’s Blog: Terry Tao is a mathematician whose work is frequently relevant for computer scientists and computational theorists. Most of the posts are highly technical mathematical demonstrations that are not accessible to layman. This makes his blog an intellectually challenging but fruitful endeavor for the serious student of computer science or mathematics. Highlight: Derived Multiplicative Functions […]
27 November, 2017 at 3:55 am
Топ-30 лучших блогов о программировании и вычислительной технике — Rus.Rocks
[…] Что почитать на Terry Tao’s Blog: Производные мультипликативные функции […]
13 December, 2017 at 9:27 am
Sean Lynch
Regarding remark 1, do you mean the logarithmic derivative of an Euler product?
[Corrected, thanks – T.]
19 January, 2021 at 4:46 am
asahay22
Unless I’ve misunderstood something, it appears to me that 1-derived multiplicative functions are precisely the functions that arise as the coefficients of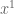 in for a multiplicative function
in for a multiplicative function ![f:\mathbb{N} \to \mathbb{C}[[x]]](https://s0.wp.com/latex.php?latex=f%3A%5Cmathbb%7BN%7D+%5Cto+%5Cmathbb%7BC%7D%5B%5Bx%5D%5D&bg=ffffff&fg=545454&s=0&c=20201002) . This raises the question that do functions that are the coefficients of
. This raises the question that do functions that are the coefficients of 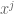 for
for 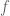 as above arise in analytic number theory or sieve theory?
as above arise in analytic number theory or sieve theory?
Also, a minor point, but I think you intended to use in the paragraph right after Remark 1.
in the paragraph right after Remark 1.